A LOOK AT INDIA’S ECONOMY AFTER THE ONSET OF AI
- Science and technology, Generative AI, Big Data, GANs, ChatGPT1 tool, DALL.E2, etc. are covered in the preliminary exams.
- Mains GS Papers III and IV: The value of technology for India, artificial intelligence (AI), localization of technology, and creation of new technology.
Summary of the Article
- Large Language Models and Generative AI have increased interest in the development of AI globally.
GSPREP ON THE ISSUE
Context
Intelligent machines (AI):
- It’s a field of computer science that studies how to simulate intelligent behaviour in machines.
- It defines the process by which machines carry out actions that, in the past, required human intelligence.
- It incorporates technologies like big data, neural networks, self-learning algorithms, pattern recognition, and machine learning.
- Some of the instances of AI that we are already surrounded by include Facebook’s facial recognition software, which recognises faces in the photographs we upload, voice recognition software, which translates our requests for Alexa, etc.
AI advancements
- Generic Adversarial Networks (GANs)
- Large Language Models (LLMs)
- Transformers with generative pre-trained (GPT)
- Creating images for experimentation
- Develop commercial products for image generation, such as DALL-E.
- ChatGPT, which generates text.
o It can provide search query results as well as compose blogs, computer code, and marketing copy.
Useful areas, restrictions, and AGI:
- Artificial intelligence (AI) systems are capable of superhuman performance on particular or “narrow” tasks.
- Go is a game that is far more difficult than chess.
o For the folding of proteins in biochemistry.
- As the scope of the task is reduced, AI systems perform and function more effectively, serving as useful helpers for people.
- A few of the jobs that AI systems take on include speech recognition, translation, and even the identification of ordinary things like images. In certain cases, its performance even beats that of humans.
Limitations:
- When performing more “general” or poorly defined jobs, their performance and utility suffer.
- They struggle to incorporate conclusions drawn from various circumstances using human common sense.
- AGI, or artificial general intelligence
o It alludes to intelligence that is not constrained or specific.
o There are currently no credible efforts to develop AGI.
- Humans use common sense to preserve their lives in life-threatening situations, whereas robots may stay impassive.
ChatGPT:
- It is a generative AI tool that creates text using a Large Language Model (LLM).
- To create a statistical “model,” LLMs are huge artificial neural networks that take in a lot of digital text.
- Companies like Google, Meta, Amazon, and others have created a number of LLMs.
- ChatGPT is producing perfect paragraphs that attracted attention from all over the world.
o It could now outsource writing.
- “sparks of AGI” in GPT-4; AGI may soon appear from a larger LLM.
What worries exist?
- Ethical discussions surrounding the usage of generative AI, which gives users an advantage over non-users due to its “productivity-powered” nature.
- The Internet once went through a spiral where the topics of worker replacement and economic growth with the rise of AI entered.
Adoption of AI has positive benefits, according to many universities’ studies
- There is broad agreement that implementing AI in the production of products and services will increase productivity.
- A study by MIT economists titled “Generative AI at Work” revealed that the use of AI technologies increased worker productivity by 14%.
- It raised customer satisfaction, which in turn improved how customer service representatives were treated and increased employee retention.
- According to experts, employees employing generative AI may not replace current workers, but those who do not upskill will be replaced.
- A survey of workers at the top 50 organisations on LinkedIn in the US reveals that nearly 70% of them believe AI has improved their ability to be quicker, smarter, and more productive.
o 32% of respondents believed that while AI’s current influence may be limited, significant gains are expected over the course of the following five years.
- MIT Professor Erik Brynjolfsson contends that in order to realise the full productivity potential of AI, corporate procedures must be restructured and funding must be raised.
- The majority of research on the effects of AI on growth is upbeat.
- A PricewaterhouseCoopers (PwC) study projected that continuous AI technical breakthroughs would enhance global GDP by 14%, or $15.7 trillion, by 2030.
- A report by Goldman Sachs Research (April 2023) claimed that over a ten-year period, generative AI alone may increase global GDP by 7%, or over $7 trillion.
- It emphasises how generative AI can produce output that resembles that of a human.
- Its capacity to remove obstacles to communication between humans and machines could have significant macroeconomic benefits.
- The Forum for Kent A. Clark Centre for Global Markets: It polled and published opinions from American and European economists on how AI will affect per capita income in the US and western Europe.
o A large increase was predicted by 44% of the American experts, while 46% stated it was unclear what the implications would be.
o While 42% of European experts were unsure about the effects of AI, 34% predicted a significant boost in GDP per person.
o Only 2% of experts said AI wouldn’t have a big influence on GDP per person;
Ban on chatbots using generative AI:
Only 2% of the European experts disagreed with the statement that a ban may impede innovation, while 14% were unsure.
AI technology drawbacks (research and analysis):
- The ability of AI technologies to replace labour.
o With generative AI, even creative work may be completed quickly and efficiently. AI can automate repetitive jobs.
- The adoption of robots has a negative impact on workers, according to a study by MIT and Boston University titled “Robots and Jobs (Evidence from US Labour Markets)”.
o On average, it lowers employment, salaries, and the labour share.
o It primarily affects people with lesser levels of education and blue-collar workers.
- In the article “Tasks, Automation, and the Rise in U.S. Wage Inequality: In the previous forty years, between 50% and 70% of changes in the U.S. wage structure can be linked to relative salary decreases of worker groups specialised in repetitive tasks in industries witnessing fast automation.
- Acemoglu contends that automation lowers the labour share and wages, particularly when productivity gains are modest.
- His other research emphasise distributional automation worries.
- Contributing to worker inequality and posing major risks to societal wellbeing.
- According to a report from the European Parliamentary Research Service, AI may increase competition and widen the technology gap between enterprises. This conclusion is supported by research from the McKinsey Global Institute.
- The Guardian: The publication asserts that AI might be extremely disruptive because middle-class, white-collar employment are more likely to be replaced by it.
o Prior technical advances forced people out of lower-paying farm employment and into higher-paying industry positions.
- According to Goldman Sachs’ analysis, 15% to 35% of jobs in the American economy might be automated.
o It provides data to demonstrate how this would not have a negative impact on the labour market.
Indian opportunities
- For the millions of Indians who labour in the sector, the deployment of AI in call centres and the software industry would not increase efficiency.
- Regulating the usage of AI is not a wise course of action because it would just discourage investments and new business potential.
- The PwC analysis predicts that China will benefit from AI the most economically, with an estimated 26% increase in GDP by 2030.
o India should put more of a priority on AI education and training.
o It might be simpler now that online education is more widely accepted in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic.
- India can benefit from the demographic dividend and fresh prospects brought on by AI.
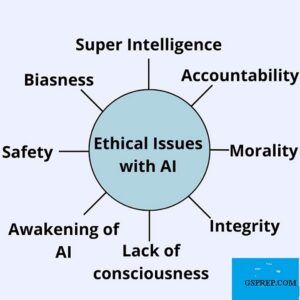
Ethics Concerning AI:
Way ahead
- India, the world’s most populous nation, should keep an eye out since any net negative impact on employment could have a negative influence on the global economy.
- AI has permeated every sphere of the global economy, and positive results are being seen in terms of productivity and growth.
- As a result of the new issues brought by AI, governments would need to tighten existing cyber rules. Many experts have also advised that governments impose capital taxes to balance the returns from capital and labour and lessen the consequences on distribution and displacement.
- AI is advancing at an exponential rate, and arming ourselves with the newest tools will help us keep up with the rest of the world.
PRACTISE QUESTION
What various components make up cyber security? Examine the extent to which India has successfully created a comprehensive National Cyber Security Strategy, keeping in mind the obstacles in cyber security. (UPSC 2022) (200 WORDS, 10 MARKS)
Source: The Hindu
